CentraLineWear System
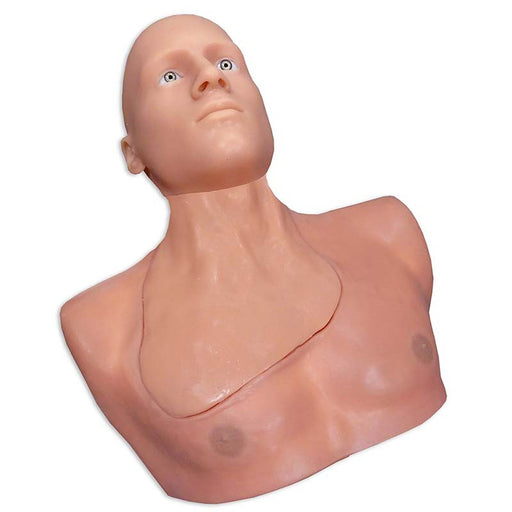
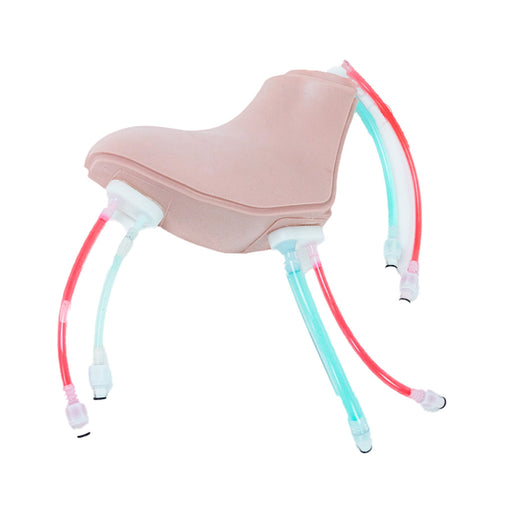
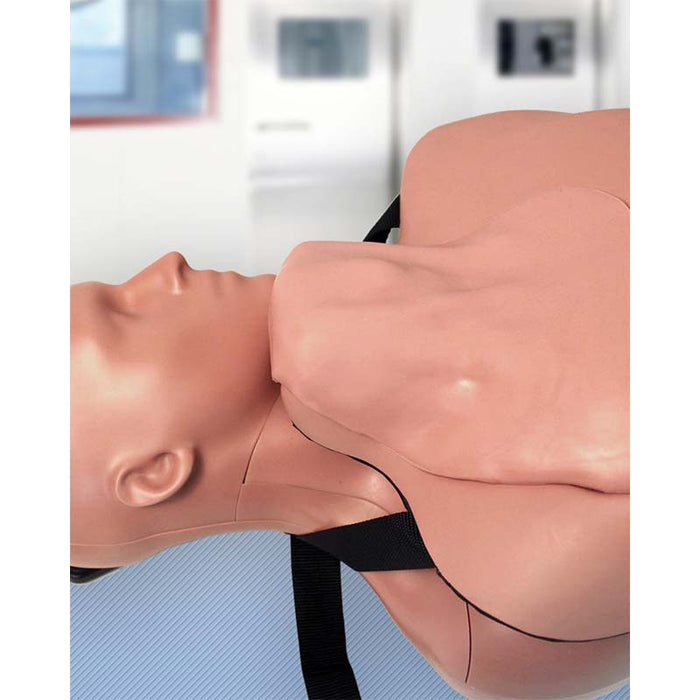
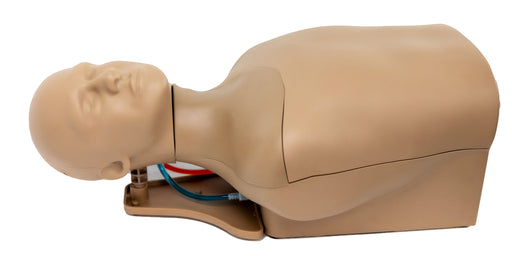
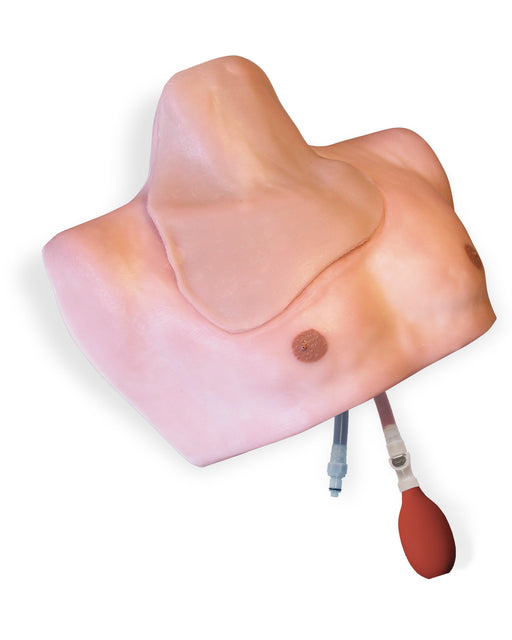
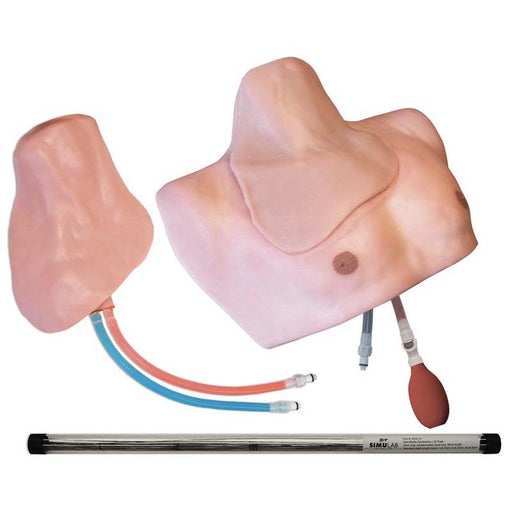
Simulab's wearable CentraLineWear System is a part of our SimuWear® collection of wearable procedural trainers. CentraLineWear is a soft-tissue central venous catheterization trainer easily and comfortably worn by Standardized Patients and used with human patient simulators.
The hardshell exterior and realistic procedural tissue have been carefully designed to keep healthcare professionals safe during interactive, hands-on CVC learning. In addition, the wearable brings all the benefits of soft-tissue procedural training to your existing simulation settings and allows for expansion of your training.
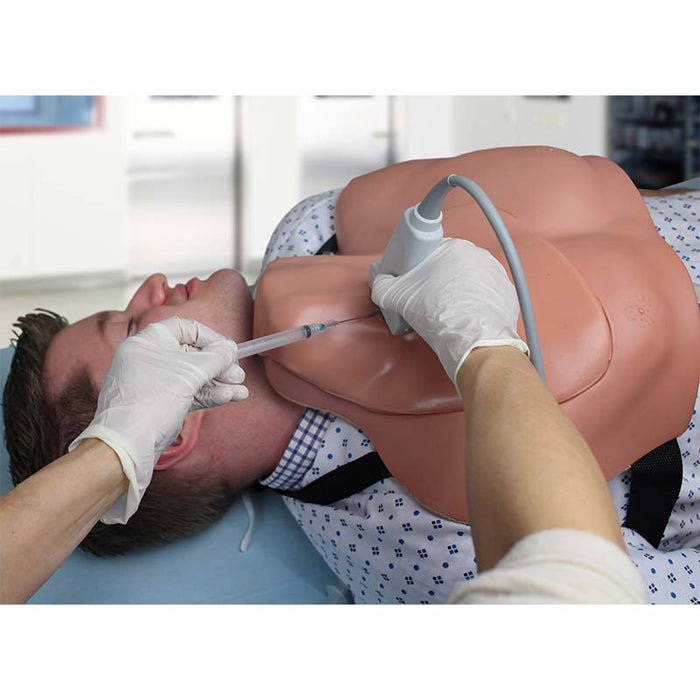
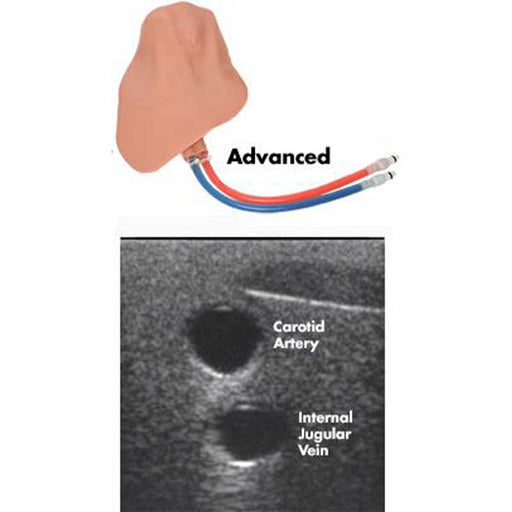
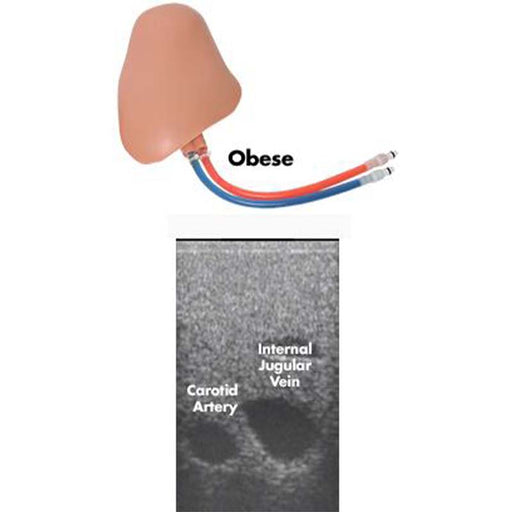
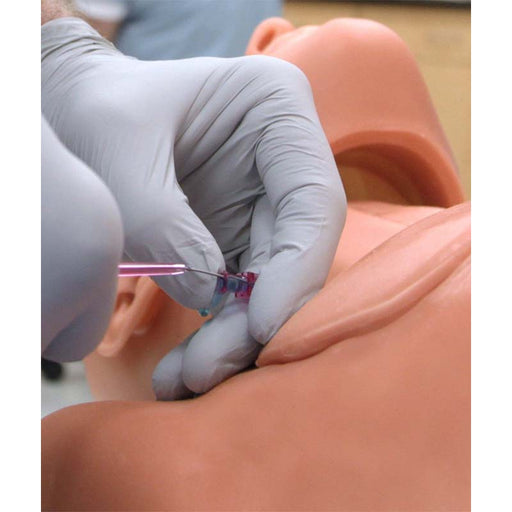
CentraLineWear features all the same clinically relevant landmarks and anatomy as CentraLineMan. Learners can practice performing full catheterization using ultrasound-guided or blind/landmark insertion approaches at the subclavian, supraclavicular, and internal jugular access sites.
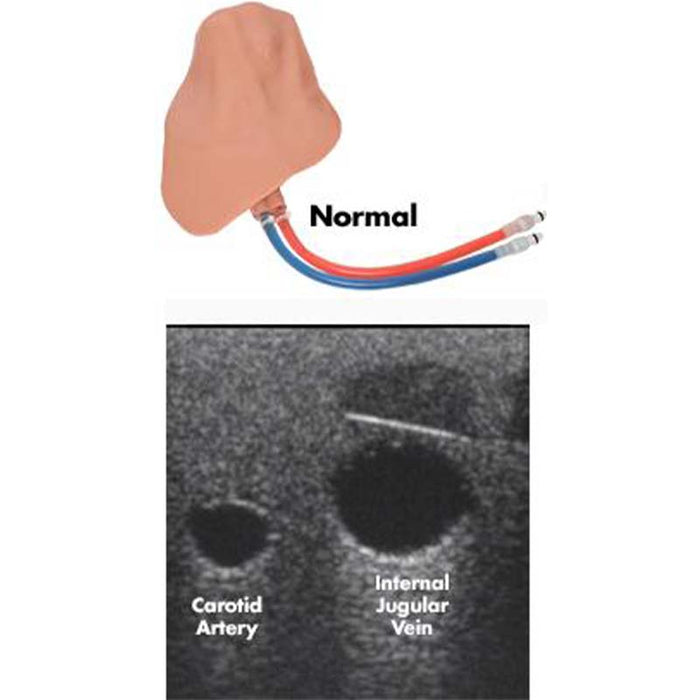
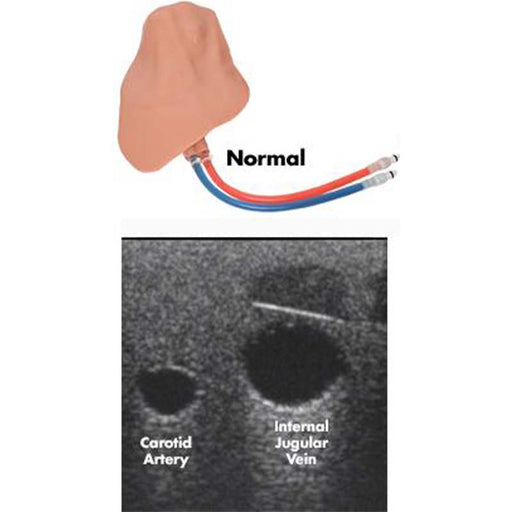
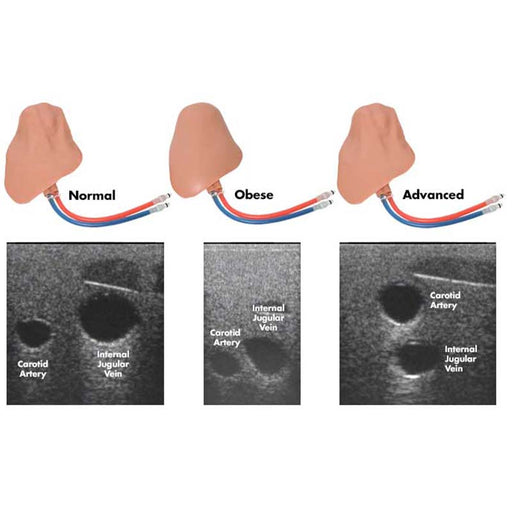
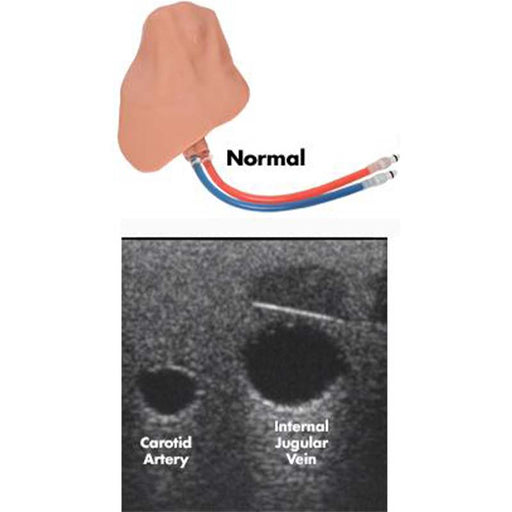
The central line simulator includes clinically relevant internal and external landmarks that are palpable or visible under ultrasound.
Relevant Anatomy Includes
- Upper torso and neck
- Trachea
- Clavicle
- Sternal notch
- Sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle
- Manubrium
- The lateral border of the first rib
- Superior vena cava
- Upper Lung
- Vascular Anatomy including the External Jugular, Internal Jugular, Subclavian, Axillary, and Brachiocephalic Veins; Carotid and Subclavian artery
- Practice full central venous catheterization using ultrasound-guided or blind/landmark insertion approaches at the subclavian, supraclavicular, and internal jugular access sites.
- Practice placing the patient in the appropriate position per access site standards
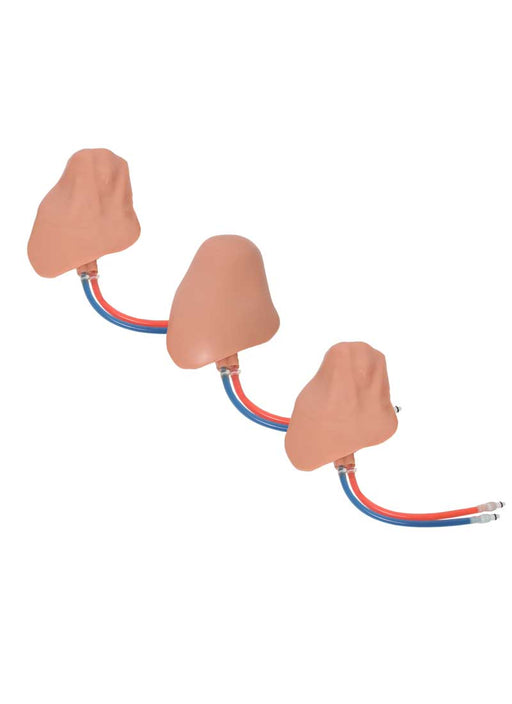
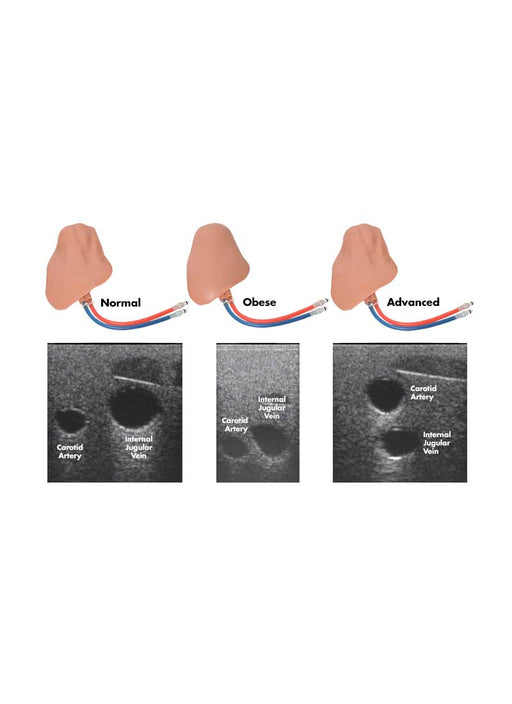
- Gain experience in identifying and selecting appropriate access site based on patient anatomical variations
- Develop psychomotor skills required for obtaining visualization during cannulation
- Detect anatomical variations
- Distinguish vessels
- Visualize arterial pulse and venous compression
- Identify the anatomical location of the target vessel
- Visualize needle cannulation of the target vessel in transverse view
- Visualize threading of guidewire in longitudinal axis view
- Visualize catheter placement
- Reduce the rate of mechanical complications due to anatomical variances such as pneumothorax or arterial puncture.
- Improve first cannulation success and decreasing needle passes
- Identify unsuccessful vessel access by fluid feedback representing arterial puncture